Plugin Command Reference
The plugin command is the CLI tool for managing Unraid plugins. It handles installation, updates, removal, and status checks.
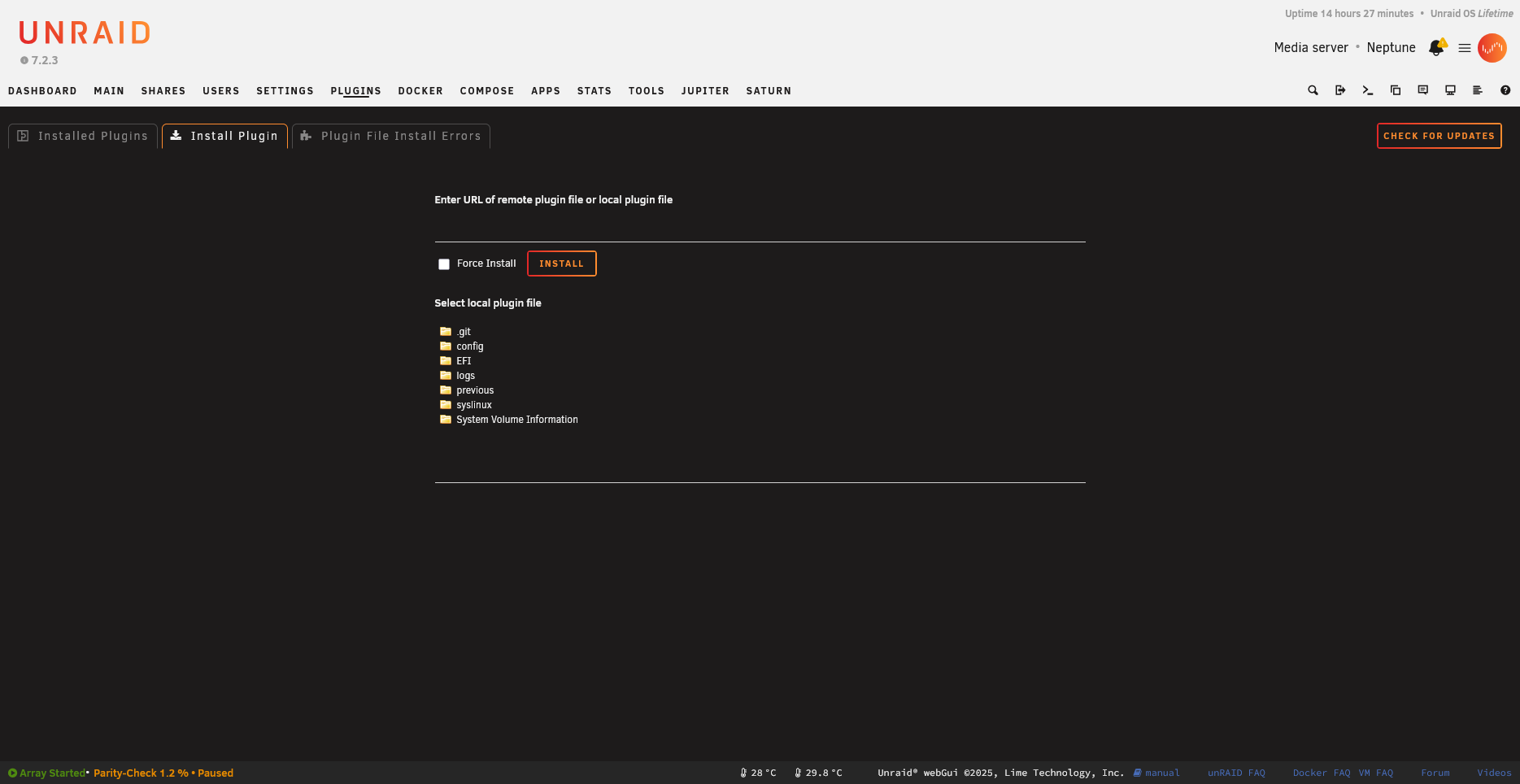
Usage: plugin install PLUGIN-FILE [forced]
plugin remove PLUGIN
plugin check PLUGIN
plugin checkall
plugin update PLUGIN
plugin [attribute name] PLUGIN-FILE
Basic Usage
plugin <command> <plugin-file>
Commands
install
Install a plugin from a local file or URL:
# From URL
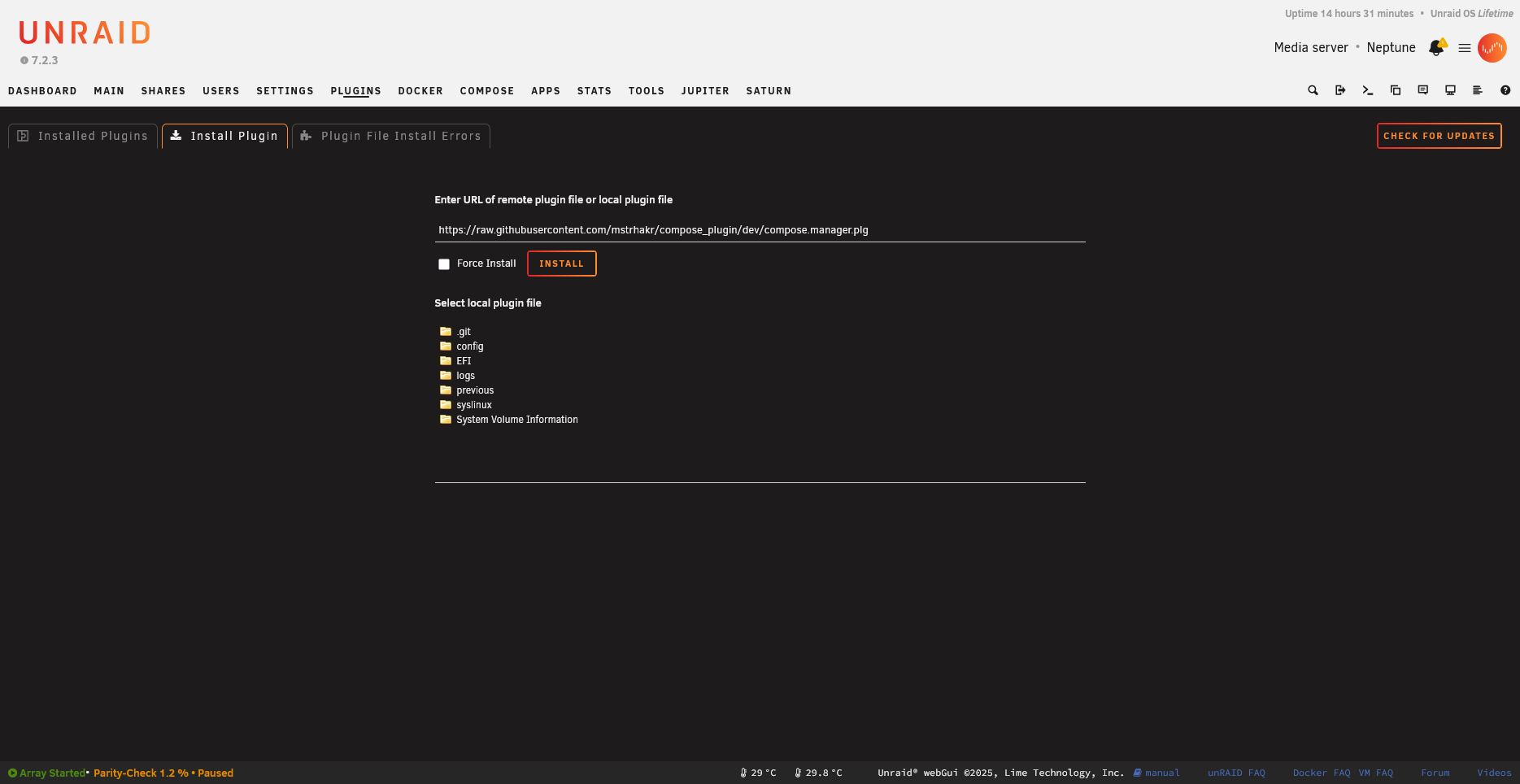
plugin install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/user/repo/main/myplugin.plg
# From local file
plugin install /path/to/myplugin.plg
# Force install (even if lower version)
plugin install /path/to/myplugin.plg forced
What happens:
- Downloads the PLG file (if URL)
- Processes all
<FILE>elements withinstallmethod - Copies PLG to
/boot/config/plugins/ - Creates symlink in
/var/log/plugins/
Install from URL:
Or upload a local file:
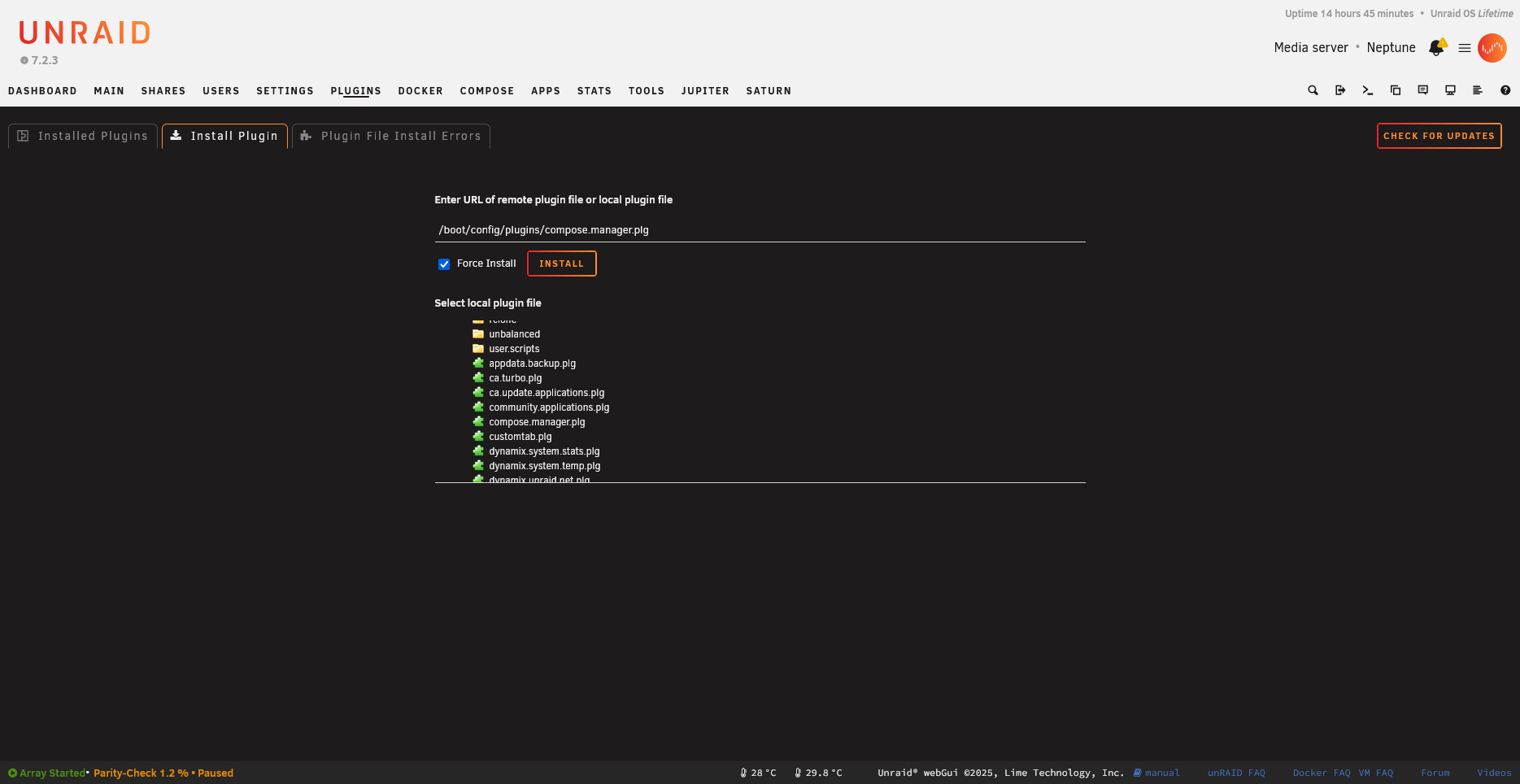
The file picker allows selecting local .plg files:

remove
Remove an installed plugin:
plugin remove myplugin.plg
What happens:
- Processes all
<FILE>elements withremovemethod - Deletes symlink from
/var/log/plugins/ - Moves PLG to
/boot/config/plugins-removed/
check
Check if a newer version is available:
plugin check myplugin.plg
What happens:
- Downloads PLG from
pluginURLto/tmp/plugins/ - Extracts and outputs the version string
- Exits 0 if newer version available
checkall
Check all installed plugins for updates:
plugin checkall
Runs plugin check for each plugin in /var/log/plugins/.
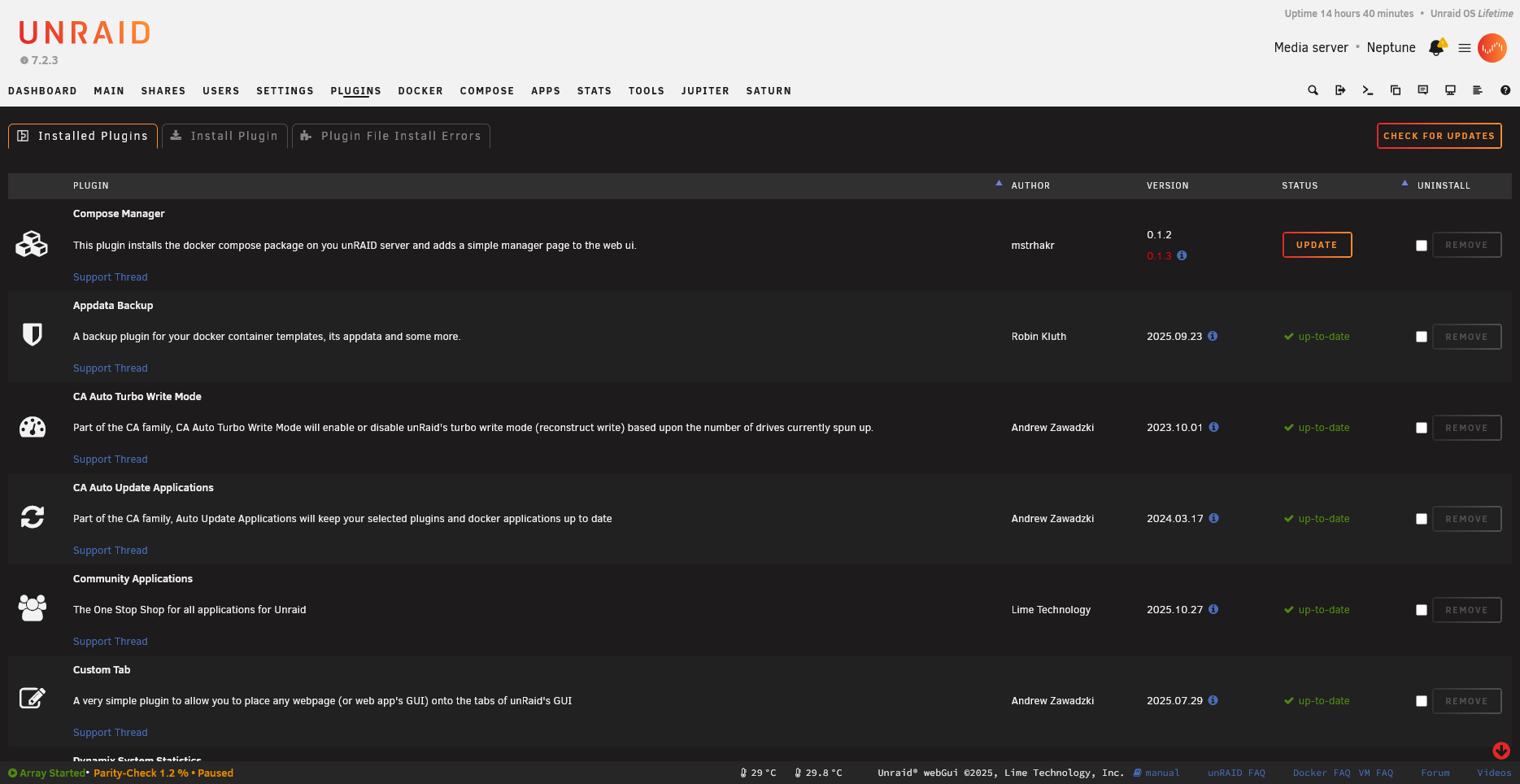
The update indicator appears next to plugins with newer versions:

After check completes, plugins with updates are highlighted:
update
Update a plugin to the latest version:
plugin update myplugin.plg
What happens:
- Looks for new PLG in
/tmp/plugins/ - Runs install method of new version
- Replaces old PLG in
/boot/config/plugins/ - Updates symlink in
/var/log/plugins/
💡 Run
plugin checkfirst to download the latest version
Attribute Queries
Get any attribute from a PLG file:
# Get version
plugin version /var/log/plugins/myplugin.plg
# Get author
plugin author /var/log/plugins/myplugin.plg
# Get any attribute
plugin pluginURL /var/log/plugins/myplugin.plg
Directory Reference
| Directory | Purpose |
|---|---|
/boot/config/plugins/ |
Active plugin PLG files |
/boot/config/plugins-error/ |
Failed installations |
/boot/config/plugins-removed/ |
Uninstalled plugins |
/boot/config/plugins-stale/ |
Superseded versions |
/tmp/plugins/ |
Downloaded updates |
/var/log/plugins/ |
Symlinks to installed plugins |
Practical Examples
Full Update Workflow
# Check for updates
plugin check myplugin.plg
# If update available, install it
plugin update myplugin.plg
List Installed Plugins
The /var/log/plugins/ directory contains symlinks to all installed plugins. Listing this directory shows you what’s currently installed on the system.
ls -la /var/log/plugins/
Check Plugin Version
Query the installed version of any plugin by passing its PLG file path to plugin version. This reads the version attribute from the PLG file’s XML header.
plugin version /var/log/plugins/myplugin.plg
Reinstall a Plugin
To reinstall a plugin cleanly, first remove it (which moves the PLG to plugins-removed/), then install from that backup location. This is useful for troubleshooting or resetting a plugin to its default state.
# Remove first
plugin remove myplugin.plg
# Then install fresh
plugin install /boot/config/plugins-removed/myplugin.plg
Debug Installation
Capture both stdout and stderr during installation for troubleshooting. The tee command displays output in real-time while also saving it to a log file for later review.
plugin install myplugin.plg 2>&1 | tee /tmp/install.log
Error Handling
Plugin Moved to plugins-error
Installation failed. Check:
- MD5 checksum mismatches
- Download failures
- Script errors
- Missing dependencies
Plugin Moved to plugins-stale
A newer version is already installed. Use forced flag if needed:
plugin install myplugin.plg forced
Update Not Working
Ensure pluginURL attribute is set in your PLG:
<PLUGIN ... pluginURL="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/user/repo/main/myplugin.plg">
Scripting with Plugin Command
Check All Updates in Script
#!/bin/bash
for plg in /var/log/plugins/*.plg; do
name=$(basename "$plg")
echo "Checking $name..."
if plugin check "$name" >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo " Update available!"
fi
done
Get Plugin Info
#!/bin/bash
PLG="/var/log/plugins/myplugin.plg"
echo "Plugin: $(plugin name $PLG)"
echo "Version: $(plugin version $PLG)"
echo "Author: $(plugin author $PLG)"
Notes
- The
plugincommand is specific to Unraid - Plugins use Slackware’s package format (
.txz) - The
upgradepkgandremovepkgcommands handle package operations - Always test plugins on a non-production server first
See Also
Full Command Reference
Complete plugin command help output
Process plugin files.
Usage: plugin install PLUGIN-FILE [forced]
install a plugin
PLUGIN-FILE is a plugin definition XML file with ".plg" extension.
PLUGIN-FILE can be a local file, or a URL. If a URL, the plugin file is first downloaded to /tmp/plugins.
forced is optional and can be used to install a lower version than currently running.
This command will process all FILE elements in PLUGIN-FILE which are tagged with the "install" method (or
that have no method tag).
This command has two major use cases:
1) Invoked at system startup by /etc/rc.d/rc.local on each .plg file found int /boot/config/plugins.
Upon success we register the plugin as "installed" by creating a symlink to it in /var/log/plugins.
If any kind of error, we move the file to /boot/config/plugins-error.
If a symlink already exists for the plugin file, this indicates a plugin replacing a "built-in" plugin. In
this case, if the version of PLUGIN-FILE is newer than the built-in plugin, we go ahead and install normally;
otherwise, we move to /boot/config/plugins-stale.
2) Invoked manually or via Plugin Manager for a .plg file not in /boot/config/plugins.
If a symlink already exists for the plugin file, this indicates a plugin update. In this case, if the version of
PLUGIN-FILE is newer than the built-in plugin, we go ahead and install normally and then move the old plugin
to /boot/config/plugins-stale.
Upon success we copy PLUGIN-FILE to /boot/config/plugins and register it as "installed" by creating a
symlink to it in /var/log/plugins.
Usage: plugin remove PLUGIN
remove a plugin
PLUGIN is the file basename of a plugin, e.g., "myplugin.plg".
If PLUGIN is found in /var/log/plugins then this command will process all FILE elements in PLUGIN which are
tagged with the "remove" method. Upon success we delete /var/log/plugins/PLUGIN and move the plugin
file to /boot/config/plugins-removed
Usage: plugin check PLUGIN
check and output the latest version of PLUGIN
We extract the pluginURL attribute from PLUGIN and use it to download (presumably the latest
version of) the plugin file to /tmp/plugins/ directory, and then output the version string.
Usage: plugin checkall
check all installed plugins
Runs 'plugin check PLUGIN' for each plugin file linked-to in /var/log/plugins.
Usage: plugin update PLUGIN
update the plugin
We look for the new plugin in /tmp/plugins/ directory. If found then we first execute the "install"
method of each FILE in the new plugin. (If necessary, a plugin can detect that this is an
"update" by checking for the existence of /var/log/plugins/PLUGIN.) If successful, we
delete the "old" plugin file from /boot/config/plugins/, copy the "new" plugin file from
/tmp/plugins/ to /boot/config/plugins/, and finally create the new symlink.
Note: to support `plugin check` and `plugin update` the plugin file must contain both "pluginURL" and
"version" attributes.
Usage: plugin [attribute name] PLUGIN-FILE
Any method which is not one of the actions listed above is assumed to be the name of an attribute of
the <PLUGIN> tag within PLUGIN-FILE. If the attribute exists, its value (a string) is output and the command
exit status is 0. If the attribute does not exist, command exit status is 1.
The plugin manager recognizes this set of attributes for the <PLUGIN> tag:
name - MANDATORY plugin name, e.g., "myplugin" or "my-plugin" etc.
This tag defines the name of the plugin. The name should omit embedded information such as architecture,
version, author, etc.
The plugin should create a directory under `/usr/local/emhttp/plugins` named after
the plugin, e.g., `/usr/local/emhttp/plugins/myplugin`. Any webGui pages, icons, README files, etc, should
be created inside this directory.
The plugin should also create a directory under `/boot/config/plugins` named after the plugin, e.g.,
`/boot/config/plugins/myplugin`. Here is where you store plugin-specific files such as a configuration
file and icon file. Note that this directory exists on the users USB Flash device and writes should be
minimized.
Upon successful installation, the plugin manager will copy the input plugin file to `/boot/config/plugins`
on the users USB Flash device, and create a symlink in `/var/log/plugins` also named after the plugin,
e.g., `/var/log/plugins/myplugin`. Each time the unRaid server is re-booted, all plugins stored
in `/boot/config/plugins` are automatically installed; plugin authors should be aware of this behavior.
author - OPTIONAL
Whatever you put here will show up under the **Author** column in the Plugin List. If this attribute
is omitted we display "anonymous".
version - MANDATORY
Use a string suitable for comparison to determine if one version is older/same/newer than another version.
Any format is acceptable but LimeTech uses "YYYY.MM.DD", e.g., "2014.02.18" (if multiple versions happen
to get posted on the same day we add a letter suffix, e.g., "2014.02.18a").
pluginURL - OPTIONAL but MANDATORY if you want "check for updates" to work with your plugin
This is the URL of the plugin file to download and extract the **version** attribute from to determine if
this is a new version.
More attributes may be defined in the future.
Here is the set of directories and files used by the plugin system:
/boot/config/plugins/
This directory contains the plugin files for plugins to be (re)installed at boot-time. Upon
successful `plugin install`, the plugin file is copied here (if not here already). Upon successful
`plugin remove`, the plugin file is deleted from here.
/boot/config/plugins-error/
This directory contains plugin files that failed to install.
/boot/config/plugins-removed/
This directory contains plugin files that have been removed.
/boot/config/plugins-stale/
This directory contains plugin files that failed to install because a newer version of the same plugin is
already installed.
/tmp/plugins/
This directory is used as a target for downloaded plugin files. The `plugin check` operation
downloads the plugin file here and the `plugin update` operation looks for the plugin to update here.
/var/log/plugins/
This directory contains a symlink named after the plugin name (not the plugin file name) which points to
the actual plugin file used to install the plugin. The existence of this file indicates successful
install of the plugin.